end tidal co2 range in cardiac arrest
Negative Epigastric sounds Equal lung sounds Esophageal detector End tidal CO2 detector Secondary signs. In addition it has been noted that cardiac arrest causes an abrupt fall in end-tidal CO2 levels to values near zero 23.

Capnography Provides Bigger Physiological Picture To Maximize Patient Care Jems Ems Emergency Medical Services Training Paramedic Emt News
End-Tidal CO2 as a Predictor of Cardiac Arrest Survival.

. In contrast Varon et al. Measuring end-tidal CO2 in cardiac arrest patients is helpful for. After 20 minutes of advanced cardiac life support ETCO2 averaged 39 - 28 mm Hg range 0 to 12 mm Hg in patients in whom the theoretical decision was made to cease field resuscitation.
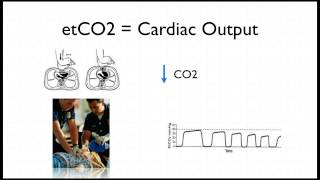
Measurement of end-tidal expiratory pressure of carbon dioxide ETCO 2 using capnography provides a noninvasive estimate of cardiac output and organ perfusion during cardiac arrest and can therefore be used to monitor the quality of CPR and predict return of spontaneous circulation ROSC. Only after the end tidal CO2 is optimized obtain an ABGVBG to verify that the pCO2 is within the target. Uses during cardiac arrest.
An intraosseous infusion was begun the trachea was intubated and end-tidal carbon dioxide tension monitoring was initiated Respironics Novametrix Wallingford CT. End tidal CO 2 monitoring is represented as a number and a graph on a monitor. Norm al EtCO2 levels 46 to 60 kPa signify adequate perfusion.
Also called capnometry or capnography this noninvasive technique provides a breath-by-breath analysis and a continuous recording of ventilatory status. In one of largest studies to date of prehospital capnography in cardiac arrest an initial EtCO2 10 mmHg 13 kPa was associated with an almost five-fold higher rate of return of spontaneous circulation ROSC. BackgroundPhysiology 2 Monitoring end-tidal CO 2 ET-CO 2 provides instantaneous information about ventilation how effectively CO.
End tidal normally 2-5 mmHg lower than arterial Comparing Arterial and End-tidal CO2 Review of Airway Confirmation Visualization Auscultation. The objective of this study was to evaluate initial end-tidal CO2 EtCO2 as a predictor of survival in out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. Because it splits into CO2 and H20 So if rises after NaHCO3 do not.
The presence of a normal waveform denotes a patent airway and spontaneous breathing. End-tidal carbon dioxide cannot be used to rule out severe injury in patients meeting the criteria. End tidal CO2 in cardiac arrest.
More common causes of cardiac arrest. End-tidal carbon dioxide ETco 2 monitoring provides valuable information about CO 2 production and clearance ventilation. MEASURING END-TIDAL CO 2 LEVELS DURING CARDIAC ARREST Presentation for MSBI Nurses Prepared by Dr.
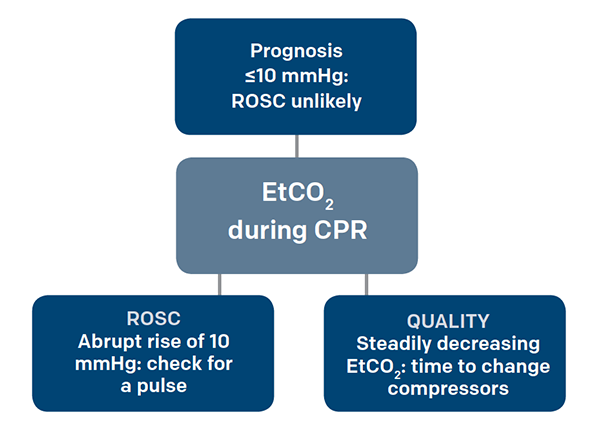
Studies have shown that in patients who had ETCO2 of 10 mmHg or less cardiac arrest was associated with death 13 14. Myocardial infarction causing VTVF. During cardiac arrest the partial pressure of end-tidal carbon dioxide PetCO2 falls to very low levels reflecting the very low cardiac output achieved with cardiopulmonary resuscitation CPR.
The primary outcome variable was attaining return of spontaneous circulation ROSC in the field. End tidal carbon dioxide CO2 correlates with cardiac output during cardiopulmonary resuscitation in cardiac arrest patients. Predicting likelihood of return of spontaneous circulation ROSC in that a persistently low ETCO2 tends to predict death whereas a high or rising ETCO2 is associated with a higher chance of ROSC.
20 mmHg at 20 minutes CPR - higher chance of ROSC. In clinical observational studies mean ETCO 2 levels in patients with ROSC are higher. 14 found that no patient who survived out-of-hospital or in-hospital cardiac arrest had an end-tidal carbon dioxide level of.
Misting increased SaO2 Types of End-Tidal CO2 Qualitative Yes or No. This was a retrospective study of all adult non-traumatic out-of-hospital cardiac arrests during 2006 and 2007 in Los Angeles California. End-tidal CO2 may be useful here as an easily and immediately measurable index of changes in cardiac output.
Surement of end-tidal carbon dioxide EtCO 2 to enhance cardiopulmonary resuscitation CPR quality and optimize blood flow during CPR. A ETCO 2 cardiac arrest. After 20 minutes of CPR death occurs if ETCO2 is consistently below 10 mmHg with 100 sensitivity and specificity 15.
In contrast survivors ETCO2 just before restoration of circulation averaged 31 - 53 mm Hg range 16 to 35 mm Hg P 0001. Because impaired circulation during arrest causes CO2 to build up in the bloodstream the initial ETCO2 reading may initially be higher than the normal 35-45 mm Hg range as it gets washed out of. Using an ETCO2 of 10 mm Hg or less as a theoretical.
Increasing CO2 during CPR can also indicate the return of spontaneous circulation. Primary ventricular arrhythmia eg VT arising from old myocardial scar torsade de pointes. Abrupt increase in ETCO2 suggests ROSC during CPR detectable before pulse check ETCO2 at 20 minutes of CPR is prognostically useful.
An increase in etCO2 by 5 appears to have reasonable sensitivity 71-91 and specificity 94-100 for fluid responsiveness in two studies of patients breathing passively on the ventilator. In fact its commonly called the ventilation vital sign. This will generally put the pCO2 into a safe range.
Except for a brief period during which the end-tidal carbon dioxide tension was in the range of 13 to 21 mm Hg the measurement was in the 28 to 35 mm Hg range consistent with. Gradual fall in ETCO2 suggests compressionist fatigue during CPR - time to change compressionists. Numerous factors impact EtCO 2 eg ventilation metabolism cardiac output yet few clin-ical studies have correlated CPR quality and EtCO 2 dur-ing actual out-of-hospital cardiac arrest OHCA resuscita.
The purpose of this systematic review is to evaluate the prognostic value of ETCO2 during cardiac arrest and to explore whether ETCO2 values could be utilised as a tool to predict the outcome of resuscitation. The number is called capnometry which is the partial pressure of CO 2 detected at the end of exhalation ranging between 35 - 45 mm Hg or 40 57 kPa. CO2 will decrease prior to a cardiac arrest in patients that are intubated in an intensive care setting.
Waveform and end -tidal carbon dioxide EtCO2 values. Capnography can be used to assess unresponsive patients ranging from those are actively seizing to victims of chemical terrorism. An accurate early predictor of the outcome of resuscitation is needed.
Pierre Kory Laura OBrien RN CNS. In addition a decrease in the EtCO2 during resuscitative events of 25 was associated with a. Literature search was performed using Medline and EMBASE.

Reversible Causes Of Low Etco2 In Cpr Criticalcarenow

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project

Average Etco2 Kpa During Cpr In Patients With Or Without Rosc Download Scientific Diagram
Use Capnography For A Patient In Cardiac Arrest Capnoacademy Capnoacademy
Use End Tidal Capnography For Placing Orogastric Nasogastric Tubes And Cpr Page 2 Of 4 Acep Now Page 2

3 Waveform Capnography Showing Changes In The End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Download Scientific Diagram

Etco2 Valuable Vital Sign To Assess Perfusion The Airway Jedi
End Tidal Co2 Monitoring In The Pre Hospital Environment More Than Just Endotracheal Tube Placement Confirmation Journal Of Paramedic Practice

3 Waveform Capnography Showing Changes In The End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Download Scientific Diagram
Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Educationcapnography In The Ed Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Education

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project

Capnography During Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Current Evidence And Future Directions

References In Initial End Tidal Co2 Partial Pressure Predicts Outcomes Of In Hospital Cardiac Arrest The American Journal Of Emergency Medicine

Quantitative Waveform Capnography Acls Medical Training

Capnography Provides Bigger Physiological Picture To Maximize Patient Care Jems Ems Emergency Medical Services Training Paramedic Emt News

Sar Helicopter Paramedic Practice Etco2 Measuring To Assist With Cpr Attempts Journal Of Paramedic Practice

Clinical Rationale Textbook Hey Guy I Have Been Asked To Talk About Capnography Or Etco2 Monitoring With This Now Being Introduced For Als In Cardiac Arrest Outside Of Cardiac Arrest This
